Let me start with the conclusion: Having recently disassembled the Model 3's headlight driver module, I was thoroughly impressed by its structural design, internal hardware solution, and PCB component layout. This naturally led me to examine what Tesla's flagship Model S headlight driver module would look like. To be honest, the teardown results were quite disappointing - in my opinion, it's inferior to the Model 3's driver module solution. Of course, it's possible that the unit I disassembled was from the very first batch of Model S vehicles, and newer versions might have updated hardware solutions. If anyone has more information, please feel free to comment.
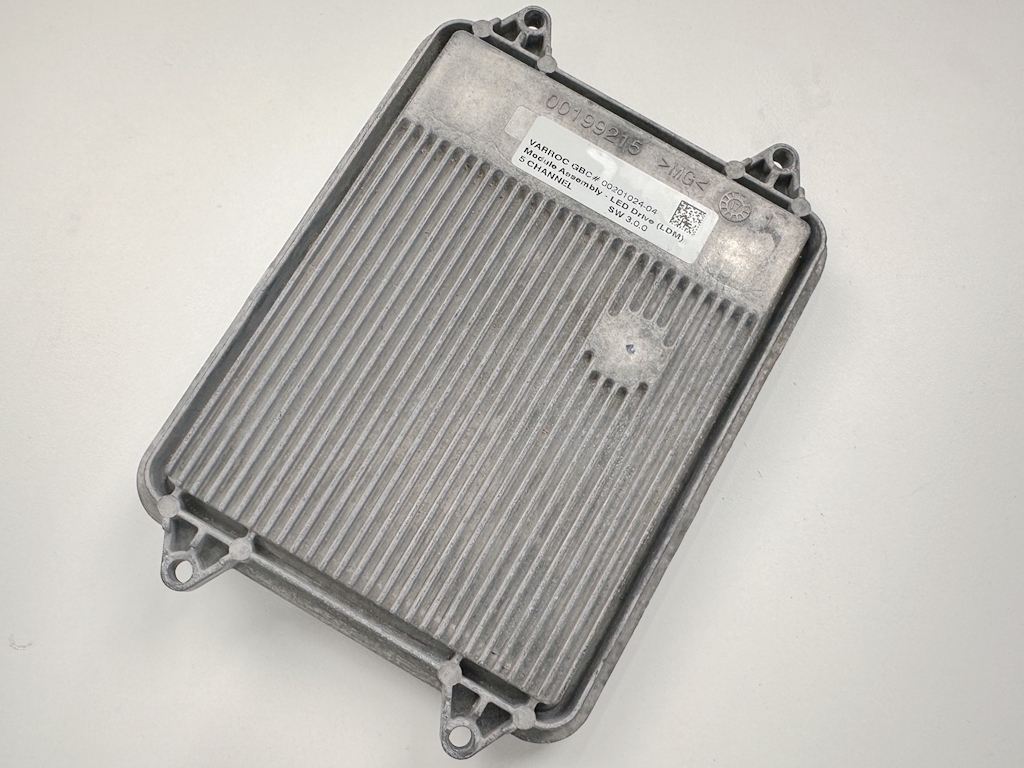

The image above shows the Model S headlight driver module we disassembled. Overall, its physical dimensions are larger than the Model 3's, resembling those of the AITO M7 and Xiaomi SU7. However, one notable issue is that this driver module appears to lack proper moisture and humidity protection features - whether this is due to previous repairs or original design remains unclear. In any case, we proceeded with the teardown.
Teardown
The internal construction, as shown below, is underwhelming—clearly showing its age.
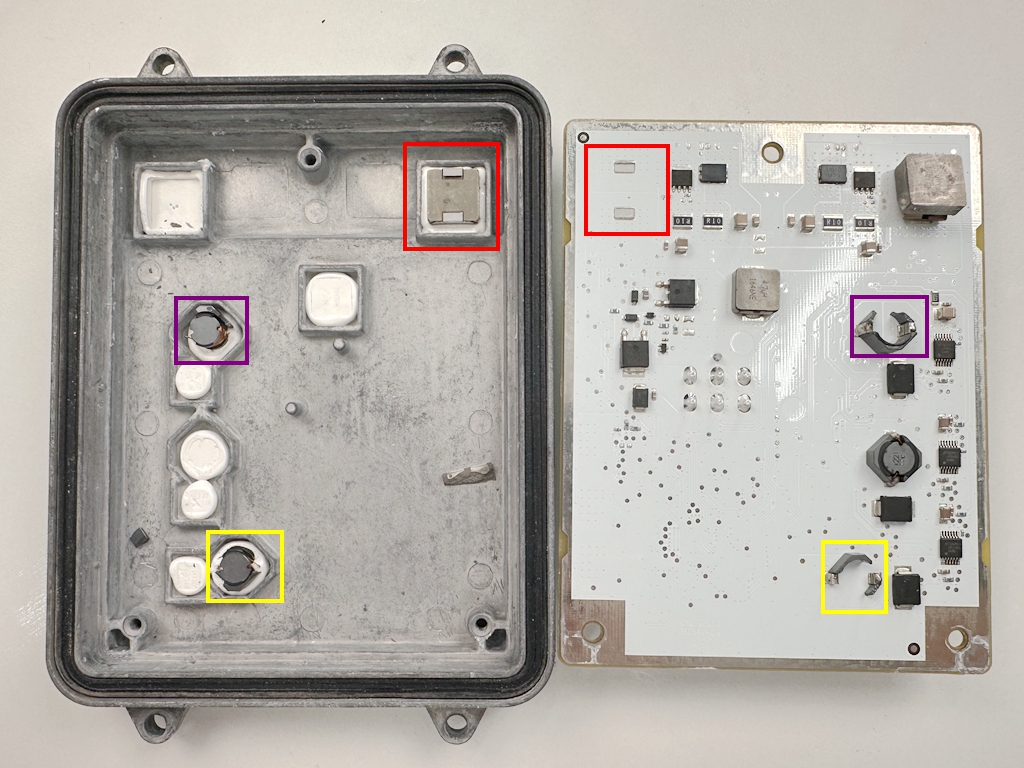
The most striking observation was the dried-out thermal paste on the heat sink, with several wire-wound inductors and a surface-mount inductor directly adhered to it. Even the PCB solder pads couldn’t withstand the aging.
The white PCB board features a spacious layout. While not optimized for compactness, this design likely improves reliability and minimizes signal interference.

Key Components on the PCB:
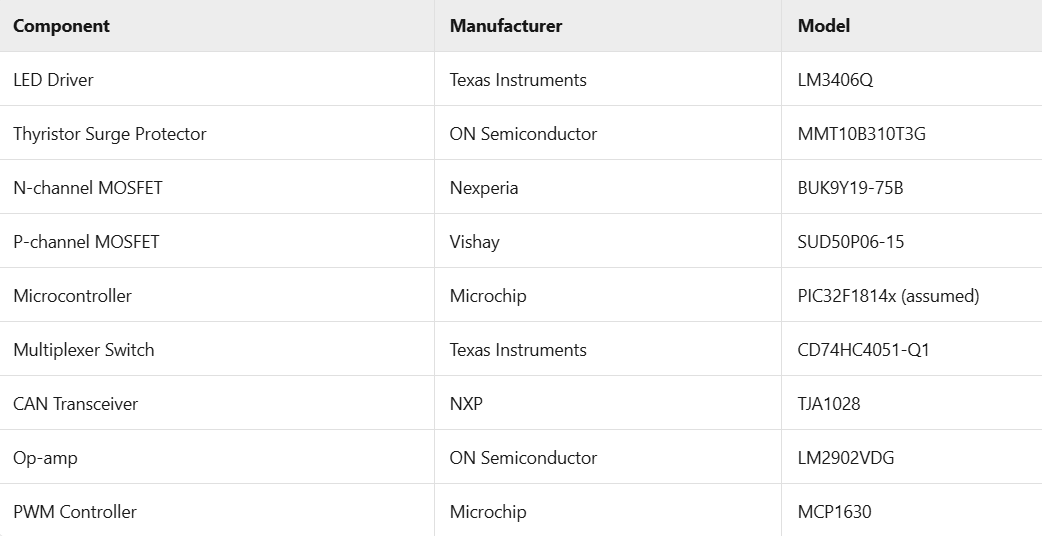
3x Texas Instruments LED driver chips (LM3406Q);
3x ON Semiconductor thyristor surge protectors (MMT10B310T3G);
2x Nexperia N-channel MOSFETs (BUK9Y19-75B);
2x Vishay P-channel MOSFETs (SUD50P06-15);
Adjacent to these are two discrete components marked "V810 M79"—anyone know their exact model?
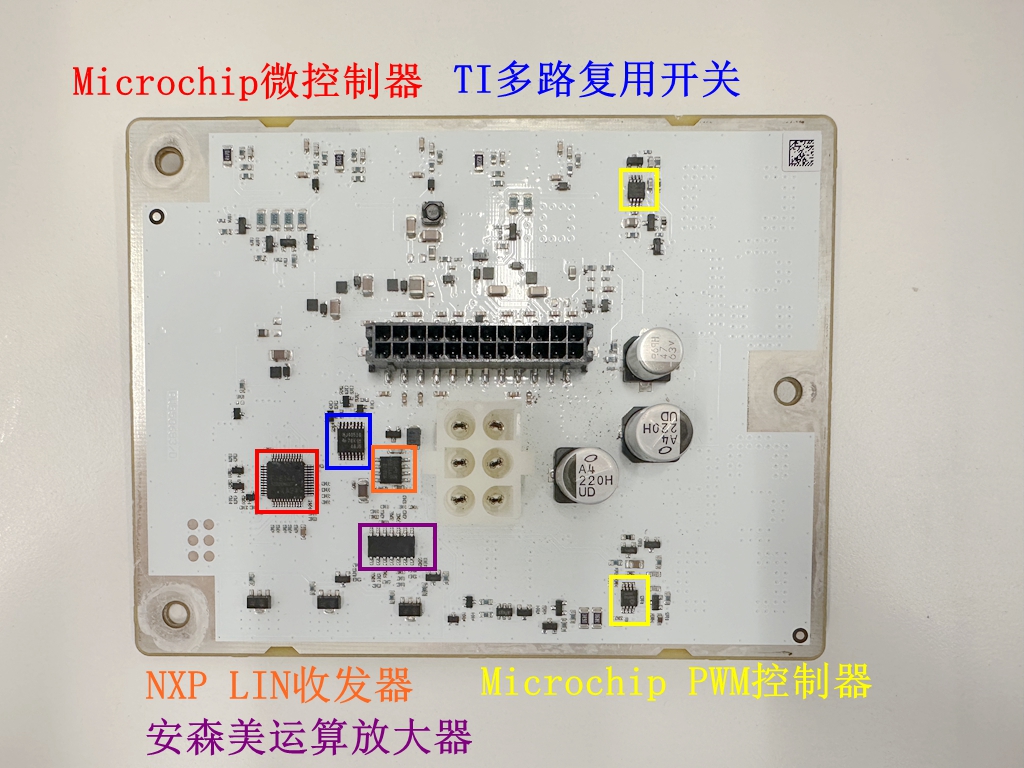
Components on the Reverse Side of the PCB:
A main control chip marked "F1814T", likely a Microchip microcontroller (PIC32F1814x);
A Texas Instruments multiplexer switch (CD74HC4051-Q1),The Model 3’s headlight driver board also uses a TI analog switch, albeit a different model.
A NXP CAN transceiver (TJA1028),Interestingly, the board only has one CAN transceiver, whereas the Xiaomi SU7’s headlight driver board uses two for redundancy—arguably a more reliable design.
An ON Semiconductor op-amp (LM2902VDG);
A Microchip PWM controller (MCP1630),Paired with the microcontroller, this enables precise power control, further supporting the assumption that the main controller is a Microchip MCU.
Summary of Key Chips in the Model S Headlight Driver Module:
Final Thoughts
Based on this teardown, it’s clear that this headlight driver board likely belongs to an early Model S variant, lacking advanced features like adaptive front lighting systems (AFS) and falling behind modern designs like the Model 3 or Xiaomi SU7.
This serves as a reminder: today’s electric vehicles are evolving at a pace reminiscent of consumer electronics. If you’re not careful, you might end up paying a premium for what quickly becomes outdated tech—a challenge for both manufacturers and consumers.
What’s your take on this somewhat antiquated headlight hardware in a luxury car?
来源: 与非网,作者: 曹顺程,原文链接: https://www.eefocus.com/article/1872137.html
 芯耀
芯耀



 1155
1155











